Learning Application Capstone Project
SongLingual
The SongLingual Project is an innovative language learning platform that harnesses the power of music to enhance English language acquisition for young ESL learners. This project demonstrates a user-centric design approach, leveraging interactive features, multimedia elements, and pedagogical elements to make language learning immersive and enjoyable.

Project Summary
The Problem
Many young ESL learners struggle with traditional language learning methods, finding them boring and disconnected from real-life contexts, which makes it harder to stay motivated and engaged.
The Solution
A music-based language learning platform that combines the power of songs with interactive features to make learning English fun, engaging, and effective. By using lyrics to teach grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and creative writing, the platform provides an immersive and enjoyable experience. Tools like Pronunciation Peninsula and Writing Waters allow learners to practice speaking, listening, and expressing themselves in a way that feels natural and connected to real-life situations, keeping them motivated and lowering the barriers to language acquisition.
The Context
Capstone project for my Learning Sciences & Technologies Master's degree (M.S.Ed).
Project Scope and Ownership
This project constitutes both a research paper and a learning product, all written, designed, and developed independently.
Project Stages
Phase One: Identify Problem Space
The initial phase of the capstone project focused on identifying the problem space related to language acquisition challenges faced by early elementary English as a Second Language (ESL) learners. This stage involved a comprehensive analysis of the problem of practice, grounded in both personal observations and an extensive review of scholarly literature.
Problem Statement
The project began by defining a critical educational challenge: traditional teaching methods often fail to engage young ESL learners effectively, leading to limited vocabulary acquisition, poor phonological skills, and a lack of fluency in English. These issues are compounded by the anxiety and lack of motivation that many young learners experience in language classrooms. The reliance on rote memorization and grammar drills does not address the developmental needs of this target population.
Target Population and Context
The target audience for this project is early elementary ESL learners navigating the complexities of learning a new language. This group was chosen due to their heightened need for engaging, context-rich, and interactive learning experiences. Observations revealed that traditional educational settings often do not provide the personalized or motivational support necessary for these learners to thrive.
Research and Insights
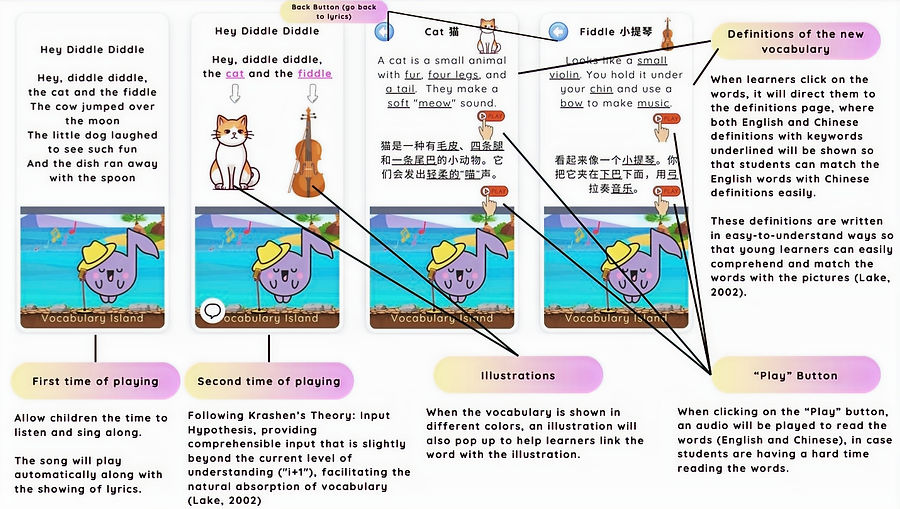
The research drew on foundational theories of second language acquisition, including Krashen's Input Hypothesis and Affective Filter Hypothesis. These theories emphasize the importance of comprehensible input slightly beyond the learner's current level (i+1) and the necessity of creating a low-anxiety, high-motivation environment for effective learning. Additional studies highlighted the potential of music-based learning to lower affective filters, enhance memory retention, and foster engagement, making it an ideal medium for addressing the challenges identified.
Phase Two: Capstone Proposal and Design Exploration
The second phase of the project focused on deeper research into potential solutions and the iterative design of a learning product tailored to the needs of early elementary ESL learners. This phase built on the insights from Phase One, refining the understanding of learner challenges and identifying strategies to address them effectively through innovative approaches.
Research Objectives
The primary objective of Phase Two was to explore and evaluate potential instructional strategies and design frameworks that could meet the specific needs of young ESL learners. The research emphasized creating an engaging, context-rich, and adaptive solution that leveraged the power of music to address challenges such as vocabulary acquisition, pronunciation, and fluency development.
Key questions included:
-
What design elements and features can effectively integrate music into language learning to enhance engagement and retention?
-
How can the product address diverse learning needs while providing personalized and interactive experiences?
-
What are the technical and practical considerations for implementing a music-based learning solution in real-world educational settings?
Literature Review and Theoretical Foundations
Building on Krashen's theories of comprehensible input and affective filters, the research delved into the role of music in educational technology. The following key insights guided the design exploration:
-
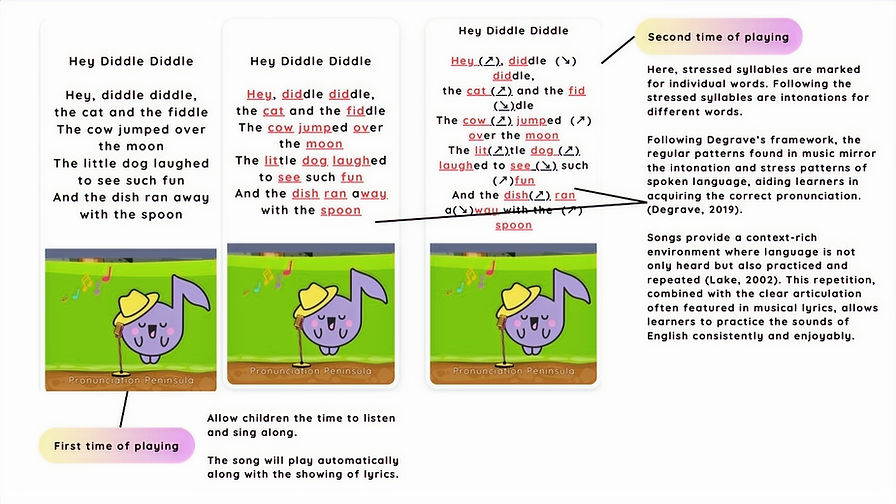
Vocabulary Development: Studies highlighted the mnemonic benefits of music in vocabulary acquisition. Songs provide repetitive and rhythmic structures that enhance memory retention and embed new words in meaningful contexts (Degrave, 2019; Paquette & Rieg, 2008).
-
Pronunciation and Listening Skills: Music's alignment with linguistic intonation and rhythm was found to improve phonological skills and listening comprehension (Zeromskaite, 2014; Falk & Dalla Bella, 2016). Singing along to songs engages learners in active auditory and phonetic practice, which reinforces accurate pronunciation.
-
Engagement and Emotional Impact: Music creates a low-anxiety, high-motivation environment that encourages participation and reduces the cognitive barriers associated with traditional language instruction (Mashayekh & Hashemi, 2011; Lake, 2002).
-
Interactive Learning Design: Incorporating interactive elements, such as games and real-time feedback, can further enhance learner engagement and provide formative assessment opportunities (Piri, 2018).
Design Exploration and Prototype Planning
The design process began with brainstorming and conceptualizing features that align with the theoretical foundations and address learner needs. The proposed solution, SongLingual, emerged as a music-based learning app with the following core components:
-
MeloAdventure Framework: The app’s central learning model was structured around four interactive zones:
-
Vocabulary Island: Focused on contextual vocabulary acquisition through songs.
-
Grammar Grove: Integrated grammar instruction with music, emphasizing rhythmic syntax learning.
-
Pronunciation Peninsula: Enhanced pronunciation and listening skills using musical intonation and stress patterns.
-
Writing Waters: Encouraged creative and reflective writing, inspired by song lyrics.
-
-
Interactive Features:
-
Voice Recording and Feedback: Allowed learners to record themselves singing along to songs and receive feedback on pronunciation and intonation.
-
Dynamic Annotations: Provided pop-up definitions, grammatical explanations, and phonetic guidance during song playback.
-
Personalized Learning Pathways: Adapted content to the learner’s proficiency level, addressing the limitations of one-size-fits-all approaches.
-
-
Gamified Elements:
-
Points, badges, and progress tracking were introduced to sustain motivation and create a sense of achievement.
-
Mini-games and matching activities reinforced key language concepts in an engaging format.
-
Link to Research Paper: https://drive.google.com/file/d/12u5WHoNgOVz5wgeCv85GHQaX5XB8ECWI/view?usp=sharing
Phase Three: Development of the Learning Product
The next phase involves the actual creation and refinement of the learning product, SongLingual, based on the insights and feedback gathered during Phase Two. This phase emphasizes building a prototype using Canva, integrating the interactive features designed during the exploration phase, and ensuring that the product is ready for testing.